
Written and collected by Zia H Shah MD, Chief Editor of the Muslim Times
In Islamic teachings, the concept of a “soul-at-peace” is referred to as an-nafs al-muṭmaʾinnah. This term describes a state of inner tranquility and contentment achieved through unwavering faith and trust in Allah. The Quran addresses such a soul in Surah Al-Fajr (89:27-30):
“O serene soul! Return to your Lord well-pleased and well-pleasing. Enter among My servants. Enter My Paradise.”
Attaining this peaceful state involves purifying the soul from negative traits and aligning one’s actions with divine guidance. Characteristics of a soul at peace include calmness, emotional balance, and a conscience that prevails over the ego. Such individuals embody human attributes to the fullest, leading lives marked by inner harmony and spiritual fulfillment. cpsglobal.org
The journey toward achieving a soul-at-peace is central to personal development in Islam, guiding believers toward a life of purpose and serenity.
The opinion of different theologians will differ about the details and many theologians may not have deep psychological insights. So, on a journey to understand soul-at-peace or an-nafs al-muṭmaʾinnah, today my goal is to develop some common secular platform, which is describing only psychological personal dimension.
In subsequent articles, we will need to add moral dimensions or interaction with the rest of humanity and, last but by no means the least, a spiritual dimension of relationship with the Divine, the Infinite, the Most Merciful, the Most Gracious, the All-Knowing, and the All-Powerful.
Abraham Harold Maslow (April 1, 1908 – June 8, 1970) was an American psychologist renowned for developing the hierarchy of needs, a theory that explores human motivation and psychological health. Born in Brooklyn, New York, Maslow was the eldest of seven children to Russian-Jewish immigrant parents. His early life was marked by loneliness and a deep immersion in books, which fostered his intellectual pursuits. pbs.org
Initially enrolling in law at the City College of New York to fulfill his father’s wishes, Maslow soon realized his passion lay elsewhere and left after his freshman year. In 1928, he married his cousin, Bertha Goodman, and the couple moved to Wisconsin. There, Maslow attended the University of Wisconsin-Madison, earning his bachelor’s degree in 1930, master’s in 1931, and Ph.D. in psychology in 1934. web.cortland.edu
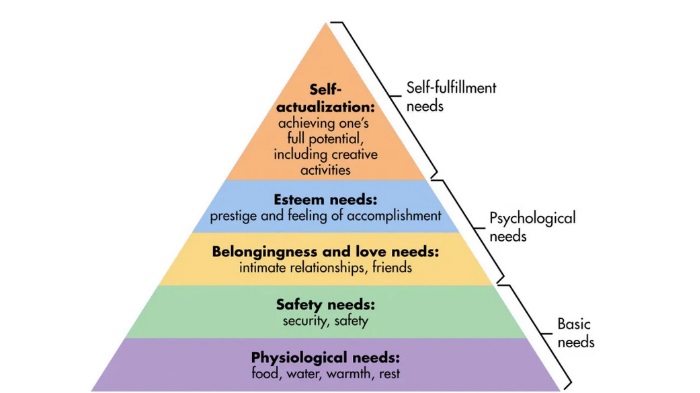
Maslow’s academic career included positions at Brooklyn College and later at Brandeis University, where he served as a professor from 1951 to 1969. It was during his tenure at Brandeis that he further developed his theories on human motivation, culminating in his seminal work on the hierarchy of needs. This model posits that human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order, starting from basic physiological necessities to the pinnacle of self-actualization—the realization of one’s full potential. britannica.com
Beyond his hierarchy of needs, Maslow was a pivotal figure in the humanistic psychology movement, emphasizing the study of healthy individuals to understand human potential and creativity. His work has profoundly influenced psychology, education, and management fields, offering insights into human behavior and motivation.
Self-actualization represents the pursuit of realizing one’s fullest potential and capabilities. This concept, prominently featured in psychologist Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, sits at the pinnacle of human development, signifying the complete realization of one’s talents, abilities, and appreciation for life. en.wikipedia.org
Self-actualization involves the realization of one’s full potential and the pursuit of personal growth and self-fulfillment. Maslow suggested that individuals striving for self-actualization are motivated by a desire to become everything they are capable of becoming. en.wikipedia.org
It’s important to note that self-actualization is not a universal experience; even if all other needs are met, it does not emerge as a motivator in all cases. When it does, it can manifest in various forms, depending on individual talents and values. britannica.com
In essence, self-actualization represents the culmination of personal development, where individuals strive to achieve their fullest potential and lead lives rich in purpose and meaning.
The concept of self-actualization has been a focal point in psychological discourse, particularly within humanistic psychology. Introduced by Kurt Goldstein and later popularized by Abraham Maslow, self-actualization refers to the process of realizing and fulfilling one’s potential. Psychologists have explored and debated this concept extensively, offering diverse perspectives on its significance and application.
Abraham Maslow’s Perspective
Abraham Maslow placed self-actualization at the pinnacle of his hierarchy of needs, suggesting that once basic and psychological needs are met, individuals strive for personal growth and self-fulfillment. He described self-actualization as the desire to become everything one is capable of becoming. Maslow’s research led him to conclude that the ability to self-actualize distinguishes the psychologically flourishing from the mediocre. He noted, “It is as if Freud supplied us the sick half of psychology, and now we must fill it out with the healthy half.” academyofideas.com
Carl Rogers’ View
Carl Rogers, another prominent figure in humanistic psychology, emphasized the importance of self-actualization in achieving personal growth and fulfillment. He believed that individuals possess an inherent tendency toward growth and that striving for self-actualization leads people to pursue happiness and fulfillment. Rogers stated, “The good life is a process, not a state of being. It is a direction, not a destination.” verywellmind.com
Viktor Frankl’s Critique
Viktor Frankl offered a nuanced perspective, suggesting that self-actualization is not an end in itself but a byproduct of finding meaning in life. He argued, “Self-actualization is not man’s ultimate destination. It is not even his primary intention. Self-actualization, if made an end in itself, contradicts the self-transcendent quality of human existence.” Frankl believed that by fulfilling meaningful goals beyond oneself, self-actualization naturally ensues. actualized.org
Contemporary Views and Criticisms
While the concept of self-actualization has been influential, it has also faced criticism for its lack of empirical support and potential cultural bias. Some scholars argue that Maslow’s hierarchy reflects Western individualistic values and may not be universally applicable. Despite these critiques, the pursuit of self-actualization continues to inspire discussions on personal development and well-being.
In summary, self-actualization remains a significant yet debated concept in psychology. While humanistic psychologists like Maslow and Rogers championed its importance for personal growth, others like Frankl emphasized the role of meaning and self-transcendence (Al Quran 59:9, 64:16). This ongoing discourse highlights the complexity of human motivation and the diverse pathways to achieving one’s full potential.
Understanding Self-Actualization
Maslow described self-actualization as the desire to become everything one is capable of becoming. This encompasses personal growth, self-improvement, and the fulfillment of intrinsic talents and abilities. Individuals striving for self-actualization seek to maximize their potential, leading to a sense of purpose and meaning in life. en.wikipedia.org
While Maslow believed achieving self-actualization is somewhat rare and posited that only about 1% of the adult population has self-actualized, current research shows this number may be higher. Further, self-actualization has not been found to correlate with age, gender, income level, or race.
He estimated that about 1-2% of individuals fully achieve self-actualization, while approximately 50% of the population is capable of reaching this level to some extent. The remaining portion of the population may not actively pursue self-actualization or may face various barriers that hinder their progress.
Means to Achieve Self-Actualization
Achieving self-actualization is a personal journey that varies for each individual. However, several common strategies can facilitate this process:
- Acceptance: Embracing oneself, others, and the surrounding world without judgment fosters a realistic understanding of one’s strengths and limitations. This acceptance enables individuals to pursue growth authentically. healthline.com
- Pursuit of Purpose: Identifying and engaging in activities that align with one’s passions and values can lead to a fulfilling and meaningful life. This pursuit often involves setting and working towards personal goals that resonate deeply. masterclass.com
- Continuous Learning: A commitment to personal development through acquiring new knowledge and skills encourages growth and self-improvement. This lifelong learning fosters adaptability and resilience.
- Authenticity: Living in accordance with one’s true self, values, and beliefs promotes inner harmony and reduces internal conflicts. Authenticity involves being honest with oneself and others, leading to genuine relationships and self-respect.
- Peak Experiences: Engaging in profound moments of love, understanding, happiness, or rapture can provide insights into one’s potential and the possibilities of life. These experiences often serve as catalysts for personal transformation.
- Cultivation of Meaningful Relationships: Building deep and authentic connections with others fosters a sense of belonging and support, which is essential for personal growth. These relationships provide encouragement, feedback, and a sense of community.
- Mindfulness and Self-Reflection: Practicing mindfulness and regularly reflecting on one’s thoughts, actions, and experiences enhances self-awareness and facilitates intentional living. This practice helps individuals stay aligned with their goals and values.
It’s important to recognize that self-actualization is not a static achievement but an ongoing process of growth and self-discovery. Individuals may experience fluctuations in their journey, but the continuous pursuit of personal development remains central to achieving self-actualization.
In summary, self-actualization involves realizing one’s full potential through acceptance, purposeful living, continuous learning, authenticity, peak experiences, meaningful relationships, and mindfulness. By embracing these strategies, individuals can embark on a fulfilling journey toward personal growth and self-fulfillment.
The theory of self-actualization is a personal psychological dimension, and we definitely need it. But there is more to human existence than our personal goals and objectives: our moral dimension, which is our interaction with the rest of humanity, and our spiritual dimension, which is our relationship with the Infinite, the Most Gracious, and the Most Merciful.
This leads us to the next article:





Leave a comment