Epigraph
وَمَا خَلَقْنَا السَّمَاءَ وَالْأَرْضَ وَمَا بَيْنَهُمَا لَاعِبِينَ
لَوْ أَرَدْنَا أَن نَّتَّخِذَ لَهْوًا لَّاتَّخَذْنَاهُ مِن لَّدُنَّا إِن كُنَّا فَاعِلِينَ
And We (Allah) created not the heaven and the earth and all that is between the two in play. If We had wished to find a pastime, We would surely have found it in what is with Us if at all We were to do such a thing. (Al Quran 21:17-18)
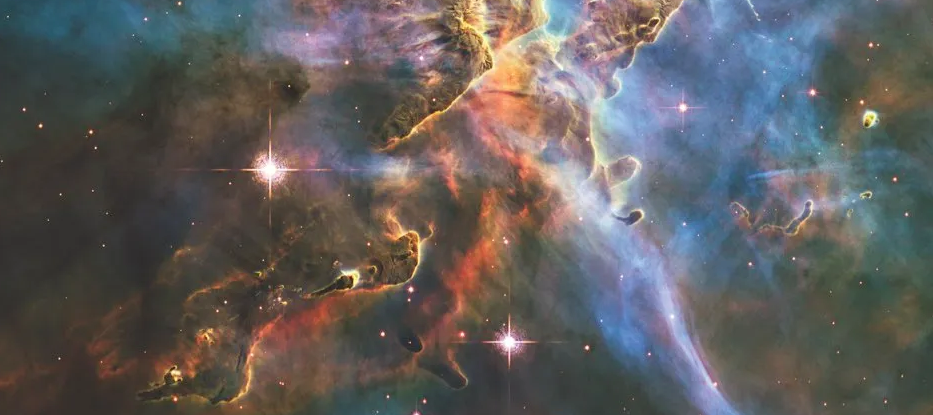

Written and collected by Zia H Shah MD, Chief Editor of the Muslim Times
When Muhammad, may peace be on him, struggled for his life and the survival of his community of less than a hundred during the first thirteen years of his ministry in Mecca, around 610 A.D., the Quran talked about interstellar clouds, not once or twice but repeatedly. One instance is mentioned as epigraph above and all the others will be pooled in the conclusion. The Arabic term used for this is وَمَا بَيْنَهُمَا, meaning what is between the heavens and the earth.
Interstellar clouds, vast accumulations of gas and dust between stars, play a crucial role in the formation of stars and planetary systems. The recognition and understanding of these clouds have evolved significantly over time, with key discoveries marking the advancement of astrophysics.
Early Observations
In the early 20th century, astronomers began to detect dark regions in the Milky Way, initially thought to be voids or “holes” in the distribution of stars. However, further observations revealed that these were not empty spaces but areas obscured by interstellar dust and gas. In 1904, the first evidence for absorption by interstellar clouds came from the analysis of a spectroscopic binary star, where certain spectral lines remained fixed in wavelength, indicating the presence of intervening interstellar gas. Physics LibreTexts
Advancements in the Mid-20th Century
The development of radio astronomy in the mid-20th century allowed for more detailed studies of interstellar clouds. In 1951, the detection of the 21-centimeter emission line of neutral hydrogen (HI) provided a powerful tool for mapping the distribution of hydrogen gas in the galaxy. This discovery enabled astronomers to study the structure and dynamics of interstellar clouds in unprecedented detail.
Modern Discoveries and Research
Recent advancements in observational technology have furthered our understanding of interstellar clouds. For instance, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has provided the darkest ever view of a dense interstellar cloud, revealing the composition of primordial ices and offering new insights into the chemical processes in some of the coldest, darkest places in the universe. ScienceDaily
Additionally, astronomers have achieved the first mapping of interstellar clouds in three dimensions, revealing the true structure of molecular clouds like Musca. This advancement not only provides a better understanding of the evolution of interstellar clouds but also aids in answering longstanding questions about star formation in our galaxy. NASA Astrobiology
Significance in Astrophysics
Understanding interstellar clouds is essential for comprehending the life cycle of stars and the evolution of galaxies. These clouds serve as the birthplaces of stars and planetary systems, and their study provides insights into the processes that lead to star formation. Moreover, the chemical composition of interstellar clouds, including the presence of complex organic molecules, has implications for the origins of life elsewhere in the universe.
Significance in biology and origin of life
Chemical compounds called nucleobases, the essential building blocks that make up DNA, have been detected for the first time in a lab-based simulation designed to mimic the gaseous clouds that are found lingering in the vast areas of space between stars.
The discovery brings us closer to understanding the origins of life on Earth, the researchers say.
“This result could be key to unravelling fundamental questions for humankind, such as what organic compounds existed during the formation of the Solar System and how they contributed to the birth of life on Earth,” said Dr Yasuhiro Oba of Hokkaido University’s Institute of Low Temperature Science, leader of the research team that made the discovery.
Conclusion
The discovery and study of interstellar clouds have been pivotal in advancing our understanding of the cosmos. The discovery and study of interstellar clouds have been pivotal in advancing our understanding of the cosmos. From early 20th-century observations to modern space telescopes, each technological leap has unveiled new aspects of these enigmatic structures, highlighting their fundamental role in the universe’s architecture, the ongoing cycle of star birth and death, and possibly the origin of life on our planet Earth.
Other references to interstellar clouds in the Quran include 15:17-18, 15:85, 20:6, 25:59, 38:10, 38:27, 38:66, 43:85, 44:7, 44:38, 46:3, 50:38, and 78:37. Revealed in seventh-century Arabia, these are indeed profound proof of the truth of the Quran.
If you are not convinced of the truth of my claim, please read the article again after reading the brief first chapter of Genesis 1.
Recent Discoveries in Interstellar Cloud Research and additional reading:
Building blocks of life could have formed in interstellar clouds




Leave a comment